what is the prognosis for malignant pleural effusion
Development of a malignant pleural effusion is associated with a very poor prognosis with median survival of 4 months and mean survival of less than 1 year. If cancer grows in the pleural space it causes a malignant pleural effusion This condition is a sign that the cancer has spread or metastasized to other areas of the body.
Malignant Pleural Effusion Still A Long Way To Go Researcher An
The presence of malignant effusion indicates advanced disease and poor survival.

. Respiratory symptoms include breathlessness cough and chest pain. Most malignant pleural effusions are secondary to metastases to the pleura most often from lung or breast cancer. This condition is associated with very high mortality with life expectancy ranging from 3 to 12 months.
This condition is associated with very high mortality with life expectancy ranging from 3 to 12 months. Sadly the average life expectancy for lung cancer with a malignant pleural effusion is less than six months. The average malignant pleural effusion life expectancy is a little less than six months with the median survival time being as less as four months.
11 Positive cytologic results on pleural lavage indicate poorer prognosis and may be incorporated into future modifications of. In lung cancer the presence of malignan. The prognosis of cases where the effusion is due to carcinoma of the lung or due to cancer of the.
The prognosis of the patient with a pleural effusion depends on the underlying condition. Pleural effusions are accumulations of fluid within the pleural space. The clinical history of patients with malignant pleural effusion MPE can be variable.
Symptomatic malignant pleural effusion is a common clinical problem. M anaging patients with malignant pleural effusion can be challenging. Asymptomatic transudates require no treatment.
Malignant pleural effusion MPE is common and is estimated to affect up to a half of patients with malignancy either at the time or during subsequent clinical course after the diagnosis of malignancy. However most patients with a pleural effusion have no long-term sequelae. Prognosis of Malignant Pleural Effusion As previously mentioned this condition often indicates the presence of advanced stage lung cancer or breast cancer.
Malignant pleural effusions are common in patients with cancer. Malignant Pleural Effusions Thoracic Key. Malignant pleural effusion MPE is common with an estimated annual incidence of 150 000 in the USA alone and given the year-on-year increase in new cancer diagnoses the incidence is set to rise1 2 MPE represents advanced malignant disease and current guidelines quote median survivals of between 3 and 12 months3 Pleural and oncological treatment options are.
MPE is a common manifestation in patients with metastatic disease and can occur in 15 of patients with cancer 23. Development of a malignant pleural effusion is associated with a very poor prognosis with median survival of 4 months and mean survival of less than 1 year. Most patients will be symptomatic although up to 25 percent may be asymptomatic with the effusion discovered incidentally during imaging for another reason.
The median survival time the time at which 50 percent of people will have died is four months though some people survive longer. Malignant effusions may change the staging and subsequent prognosis of the underlying cancer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med Vol.
Lung cancer is the most common cause of MPE followed by breast cancer lymphoma unknown primary genitourinary and gastrointestinal carcinoma. They have multiple causes and usually are classified as transudates or exudates. If due to heart failure cirrhosis or malignancy the effusion is likely to recur.
Malignant cells can reach the pleural space without effusion and lavage of the pleural space before resection of lung cancer in those without effusion can have positive cytologic results in as many as 53 in a study of 1200 patients undergoing surgery. Symptomatic malignant pleural effusion is a common clinical problem. Symptoms are often distressing and its presence signifies advanced disease.
Thoracentesis and pleural fluid analysis are often required to determine cause. The most common underlying tumors are lymphomas and cancers of the lung breast and ovaries which account for 75 of cases. It is a fairly common complication in a number of different cancers.
The main symptom of malignant pleural effusions MPE is shortness of breath 57 typically progressive exertional dyspnea followed by cough 43. Patients in these stages often have a poor prognosis with an average life expectancy of less than six months. The medial survival of patients with breast cancer was 6 months and those with either lung cancer or lymphoma had a median survival of 4 months Tables 3 and.
It is most common in lung cancer LC followed by breast cancer BC lymphoma gynecological cancers and. Median survival after diagnosis is 4 to 9 months 1 3 although prognosis varies considerably depending on the type and stage of the malignancy. This can cause you to feel short of breath andor have chest discomfort.
Dyspnea is the most common symptom of MPE. Malignant pleural effusion MPE is a common and important clinical condition. Introduction Malignant pleural effusion MPE is an effusion characterized by the presence of malignant cells 1.
Moreover mortality is higher for patients with malignant pleural effusion compared with those with metastatic cancer but no malignant pleural effusion. Malignant Pleural Effusion A malignant pleural effusion MPE is the build up of fluid and cancer cells that collects between the chest wall and the lung. A complication in many types of tumors its presence indicates the onset of the terminal stages of cancer.
Despite progress in therapeutic options the prognosis remains severe and the average survival is 4-9 months from the diagnosis of malignant pleural effusion. Detection is by physical examination and chest x-ray. Malignant pleural effusion MPE affects 150000 people in the US and over 250000 people in Europe each year and it represents a common finding up to 15 in the advanced stage cancers Lung cancer in men and breast cancer in women account for 5065 of all MPE followed by ovarian metastatic cancer hematological malignancies and malignant pleural.
The prognosis of cases where the effusion is due to carcinoma of the lung or due to cancer of the. Patients with pleural effusion and ovarian cancer had the best median survival 21 months compared with those with other primary tumors. A pleural effusion can be serious and potentially life-threatening but it is treatable.
Studies are contributing evidence on an increasing number of therapeutic options therapeutic thoracentesis thoracoscopic pleurodesis or thoracic drainage indwelling pleural catheter.
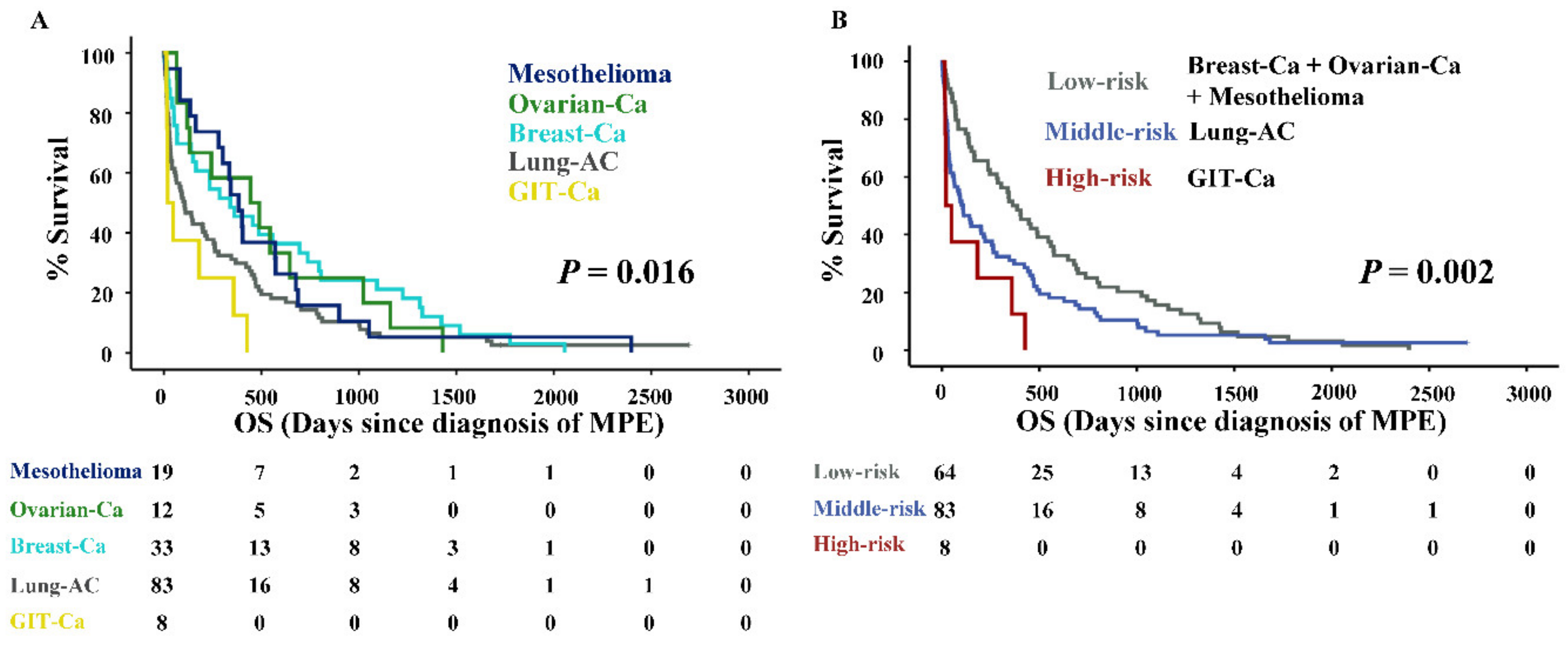
Cancers Free Full Text Prognostic Immune Cell Profiling Of Malignant Pleural Effusion Patients By Computerized Immunohistochemical And Transcriptional Analysis Html
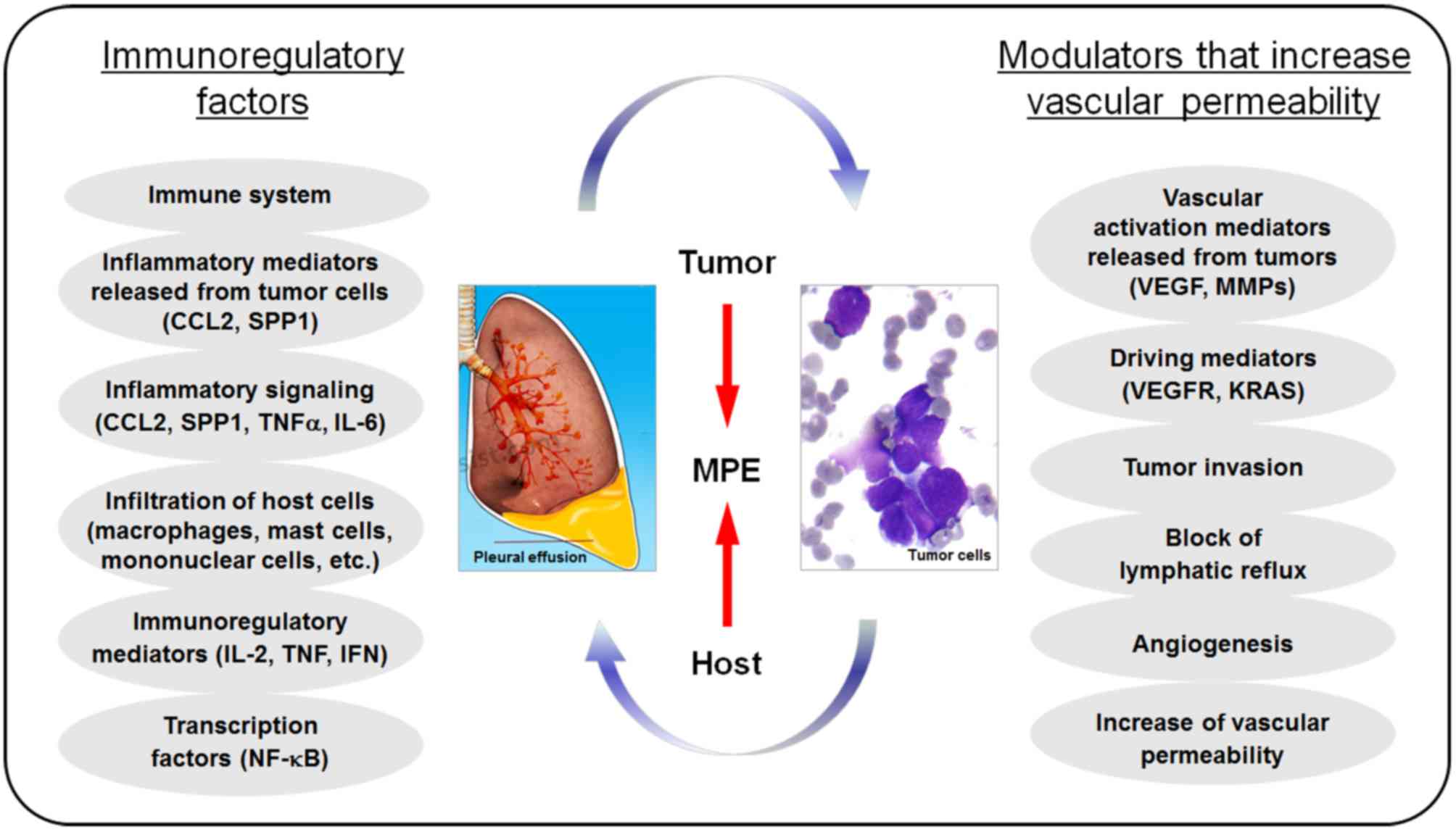
The Role Of Vegf In The Diagnosis And Treatment Of Malignant Pleural Effusion In Patients With Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Review

Ers Eacts Statement On The Management Of Malignant Pleural Effusions European Respiratory Society

Malignant Pleural Effusion Management Keeping The Flood Gates Shut The Lancet Respiratory Medicine

Prognostic Factors For Survival After Surgical Palliation Of Malignant Pleural Effusion Journal Of Thoracic Oncology
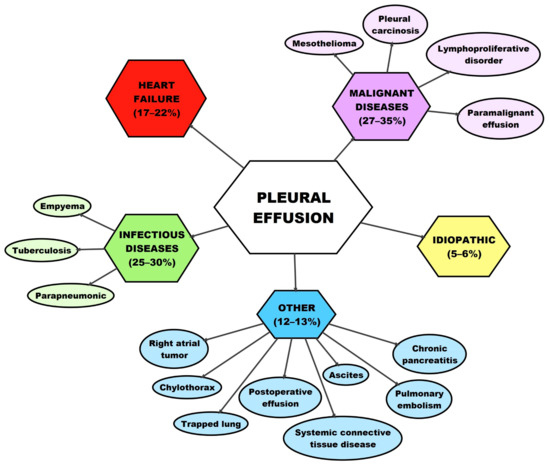
Medicina Free Full Text Malignant Pleural Effusion And Its Current Management A Review Html

Malignant Pleural Effusion 03102017 Youtube

Overall Survival Probability According To Malignant Pleural Effusion Download Scientific Diagram
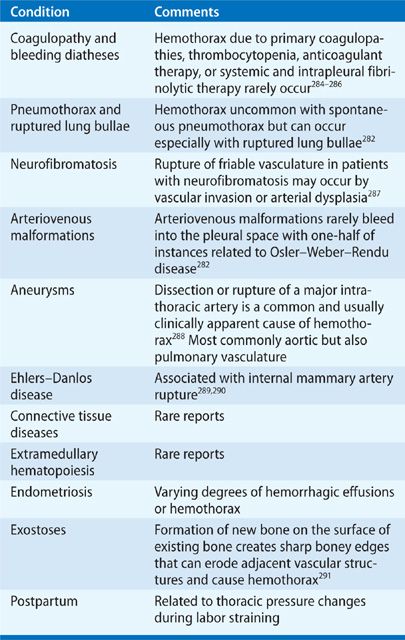
Malignant Pleural Effusions Thoracic Key

Prognostic Impact Of Malignant Pleural Effusion At Presentation In Patients With Metastatic Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Journal Of Thoracic Oncology
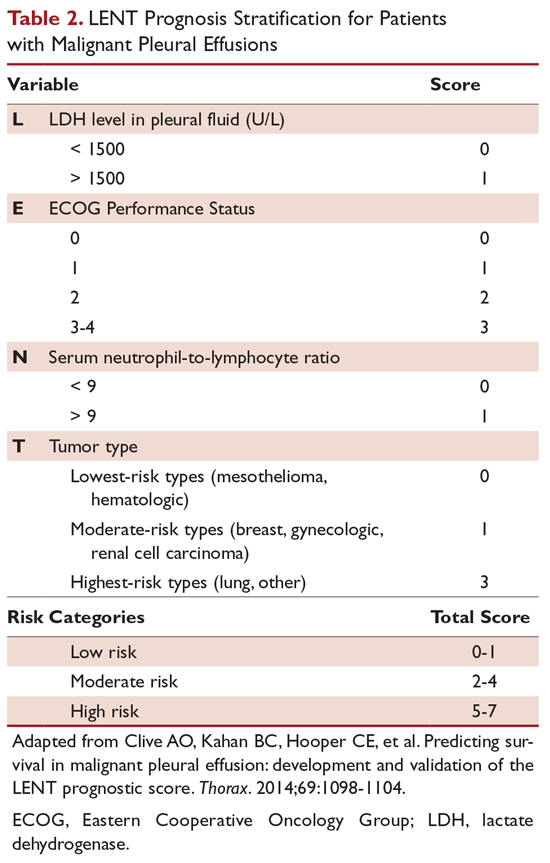
Malignant Pleural Effusion Evaluation And Diagnosis Pulmonary Health Hub

Management Of Malignant Pleural Effusions The Figure Is Modified From Download Scientific Diagram

Malignant Pleural Effusions Thoracic Key

The Diagnostic Steps In Suspected Malignant Pleural Effusion Table 1 Download Scientific Diagram

Supplemental Materials For Development And Validation Of Response Markers To Predict Survival And Pleurodesis Success In Patients With Malignant Pleural Effusion Promise A Multicohort Analysis The Lancet Oncology

Pdf Malignant Pleural Effusion Medical Approaches For Diagnosis And Management Semantic Scholar

Prognostic Factors For Survival After Surgical Palliation Of Malignant Pleural Effusion Journal Of Thoracic Oncology
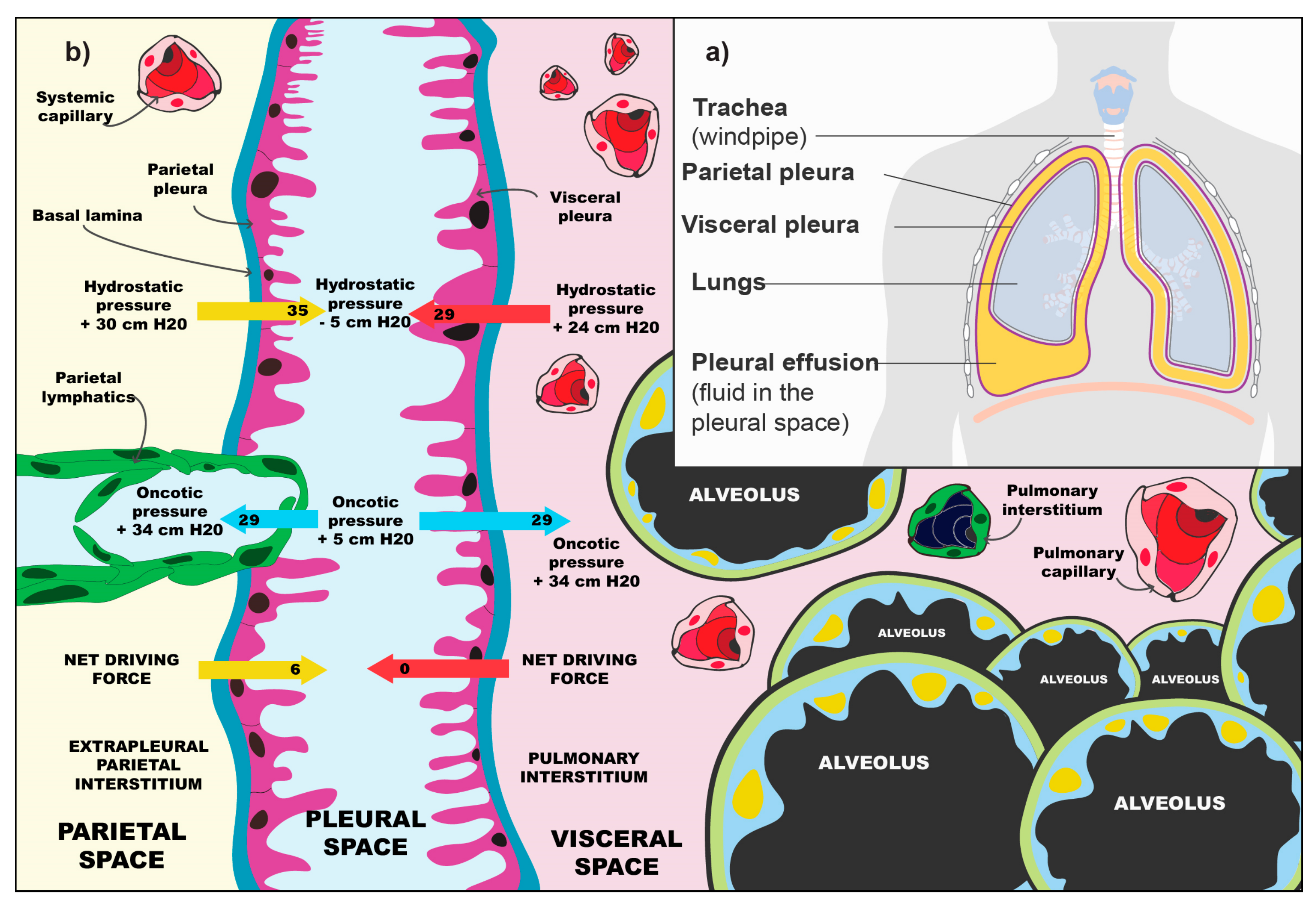
Medicina Free Full Text Malignant Pleural Effusion And Its Current Management A Review Html

Treatment Options For Malignant Pleural Effusions Download Table